Organic solar cells have the advantages of light weight, flexibility, and solution processing, and are the frontier research directions of current solar cell technology. With the rapid development of new non-fullerene acceptor materials, the energy conversion efficiency of organic solar cells has gradually improved. Recently, it has exceeded 16%, reaching a stage where it can be developed for practical application. However, the commercial application of organic solar cells still faces challenges of photovoltaic material cost and device stability. Most of the reported high-efficiency photovoltaic materials have problems such as complex structures, numerous synthesis steps, and low yields. It is difficult to meet the needs of commercial applications in terms of cost. Therefore, the development of low-cost and high-efficiency organic photovoltaic materials is a key topic for polymer solar cells toward application research. In view of this, with the support of the National Natural Science Foundation of China and the pilot project of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, the research team of Li Yongfang, the Key Laboratory of Organic Solids, Institute of Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences designed and synthesized a low-cost and efficient donor photovoltaic material PTQ10 last year The energy conversion efficiency of organic solar cells with n-type organic semiconductor (n-OS) IDIC as the acceptor reached 12.7% (Nature Commun., 2018. 9, 743., the first author is doctoral student Sun Chenkai) . However, the n-OS receptor IDIC has the problems of many synthetic steps of the central fused ring and low yield. In order to reduce the synthesis cost of the acceptor material IDIC, they developed a simplified synthesis method for the IDIC central fused ring, and at the same time, the introduction of alkoxy substituents further improved the yield of the central fused ring, and then synthesized two new low The cost of n-OS receptor molecules MO-IDIC and MO-IDIC-2F (see Figure 1 for the synthetic route). These two acceptor molecules have the advantages of narrow band gap, wide absorption and high electron mobility. Among them, the efficiency of organic solar cells prepared by blending MO-IDIC-2F with low-cost polymer donor PTQ10 reached 13.46%. They conducted cost accounting of the active layer materials for the reported high-efficiency materials, and found that solar cells based on PTQ10: MO-IDIC-2F have outstanding advantages in terms of material cost and device cost performance (see Figure 2). The above results indicate that MO-IDIC-2F is a low-cost acceptor material with application potential. Related research results were published in Nature-Communication (Nat. Commun. 2019, 10,519, the first author is doctoral student Li Xiaojun). A sensor faucet is an advanced automatic sensing device that detects hand movements and controls the flow of water through built-in sensor technology. It is an essential component of modern sanitary facilities and finds wide applications in public spaces, commercial buildings, and residential environments. Basin Faucet,Bathroom Faucet ,Sensor Faucet,Hot and Cold Faucet Jiangmen Faer Sanitary Co.,Ltd , https://www.faersanitarys.com
Fig.1 Simplified and optimized synthetic route of IDIC receptor central fused ring core 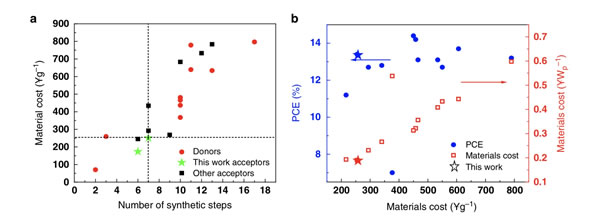
Figure 2 Comparative analysis of reported material synthesis steps, cost and efficiency in polymer solar cells
Applications:
Sensor faucets are widely used in various settings, including but not limited to:
- Public Spaces: Airports, hotels, shopping malls, hospitals, schools, etc., providing convenient and hygienic handwashing experiences.
- Commercial Buildings: Office buildings, restaurants, cafes, etc., offering efficient and water-saving faucet solutions.
- Residential Environments: Increasingly, sensor faucets are being adopted in households to enhance quality of life and hygiene standards.